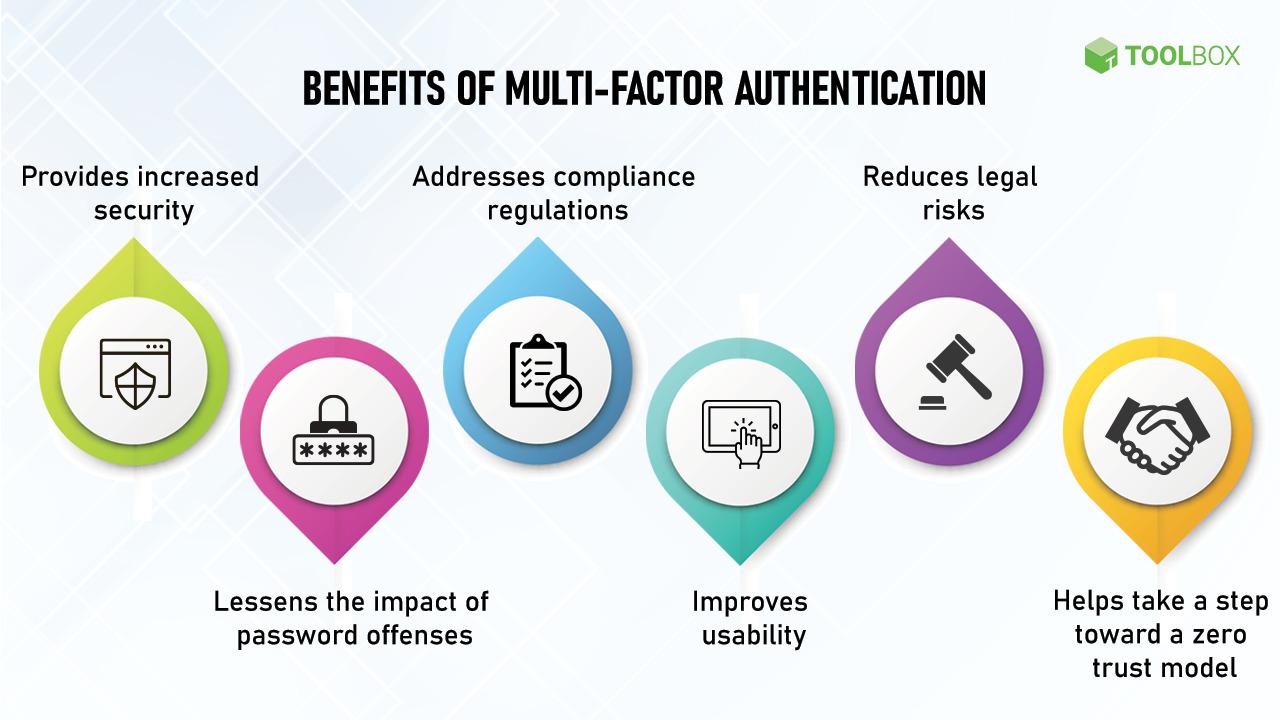
In the shadowy realm of digital security, where every click could be a potential breach, the United States Intelligence Community has spoken. A recent recommendation is sending ripples through the cybersecurity landscape: a strategic pivot in multifactor authentication methods. As technology evolves and threat actors grow increasingly sophisticated, these guardians of national digital infrastructure are signaling a critical shift that could redefine how organizations protect their most sensitive information. This unexpected guidance promises to challenge existing security paradigms and potentially reshape the future of digital authentication. In a groundbreaking move, the US intelligence community has signaled a critical shift in cybersecurity protocols, urging organizations to reassess their current multifactor authentication strategies. Recent classified reports reveal significant vulnerabilities in traditional authentication methods that have long been considered robust and dependable.
Emerging technological threats and sophisticated cyber intrusion techniques have exposed critical weaknesses in existing authentication frameworks. Intelligence analysts have identified multiple scenarios where current multifactor authentication systems demonstrate substantial security gaps that could potentially compromise sensitive governmental and corporate networks.
The recommendation stems from sophisticated hacking techniques that can now bypass conventional two-factor authentication processes. Particularly concerning are social engineering tactics and advanced phishing mechanisms that exploit human behavioral patterns and technological interconnectedness.
Cryptographic experts suggest transitioning toward more dynamic authentication models that integrate behavioral biometrics, adaptive risk scoring, and machine learning algorithms. These advanced systems would continuously evaluate user interactions, creating a more fluid and responsive security environment.
Key recommendations include implementing passwordless authentication methods, leveraging blockchain-based verification protocols, and developing more nuanced risk assessment frameworks. The intelligence agency emphasizes the importance of moving beyond static authentication models that rely solely on predetermined credentials.
Behavioral biometric technologies represent a promising alternative, analyzing unique user interaction patterns such as typing rhythm, mouse movement, and device handling characteristics. These sophisticated approaches create multi-layered authentication ecosystems that are exponentially more challenging to compromise.
Organizations across government and private sectors are expected to gradually implement these transformative authentication strategies. The transition will require significant technological investment and comprehensive training programs to ensure seamless implementation.
Cybersecurity professionals anticipate this recommendation will trigger widespread technological innovation, compelling authentication solution providers to develop more sophisticated, adaptive security frameworks. The intelligence community’s directive signals a fundamental reimagining of digital identity verification.
Financial institutions, technology corporations, and government agencies will likely be the first to adopt these advanced authentication methodologies. The potential economic impact of these changes could reshape entire cybersecurity infrastructure landscapes.
While challenges remain in developing universally applicable authentication standards, the intelligence agency’s recommendations represent a critical step toward more resilient digital security ecosystems. The ongoing technological arms race between cybersecurity professionals and malicious actors continues to drive unprecedented innovation in authentication technologies.