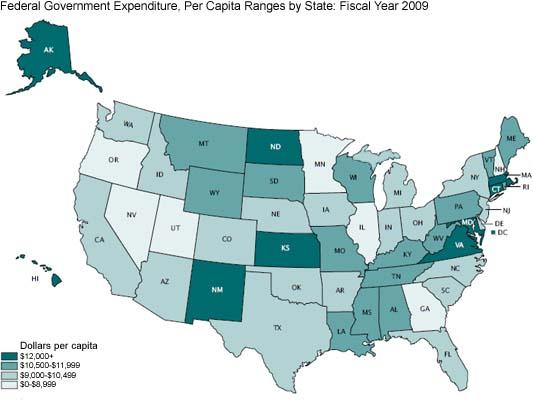
In the sprawling tapestry of American governance, federal funding weaves a complex narrative of economic interdependence and regional disparities. Some states stand as pillars of financial resilience, while others rely more heavily on the federal government’s fiscal lifeline. This exploration peels back the layers of economic dependency, revealing a nuanced portrait of state-level financial dynamics that challenge simplistic narratives of self-sufficiency and federal support. From rural landscapes to urban centers,we’ll uncover the states that lean most heavily on Washington’s financial resources,and those that chart a more independent fiscal course. In the complex landscape of U.S. state economics, federal funding plays a crucial role in supporting state budgets and infrastructure. Louisiana tops the list of most federally dependent states, receiving approximately $3,242 per capita in federal funds. Mississippi follows closely, with $3,186 per capita, relying heavily on federal support for critical services and economic stability.
New Mexico ranks third, receiving ample federal dollars primarily through defence spending, research institutions, and Native American support programs. Kentucky takes the fourth spot, with notable agricultural and infrastructure subsidies bolstering its state budget. Montana rounds out the top five, leveraging federal funds for rural advancement, agricultural support, and extensive federal land management.
On the opposite end of the spectrum, Connecticut demonstrates remarkable fiscal independence, receiving the least federal funding per capita. The state’s robust financial services sector and high-income population contribute to its economic self-sufficiency. New Jersey follows,with a strong industrial base and diverse economic opportunities reducing federal dependency.
Massachusetts ranks third among least dependent states, driven by its thriving technology and education sectors. Its world-renowned universities and innovative industries generate substantial local revenue. Illinois sits fourth, leveraging a robust manufacturing and service economy that minimizes federal reliance.
California completes the list of least federally dependent states, despite its massive population. The state’s technology hub, entertainment industry, and agricultural exports create significant economic resilience. These states demonstrate that strategic economic development and diverse industry portfolios can significantly reduce federal funding requirements.
Factors influencing federal dependency include local tax bases, industrial diversity, population demographics, and economic infrastructure. States with robust, multi-sector economies tend to require less federal intervention. Conversely, states with limited economic opportunities or significant rural populations often rely more heavily on federal support.
Economic policy experts suggest that reducing federal dependency requires targeted investment in education, technology, and entrepreneurship. By developing local industries and creating competitive job markets, states can gradually decrease their reliance on federal funding.
This federal funding landscape reveals complex economic dynamics across different U.S. regions. While some states require substantial federal support, others have developed complex economic strategies that minimize external financial dependencies.Understanding these patterns provides insights into state-level economic resilience and potential growth strategies.
The ongoing challenge for state governments remains balancing federal support with local economic development initiatives, ensuring sustainable growth and financial independence.