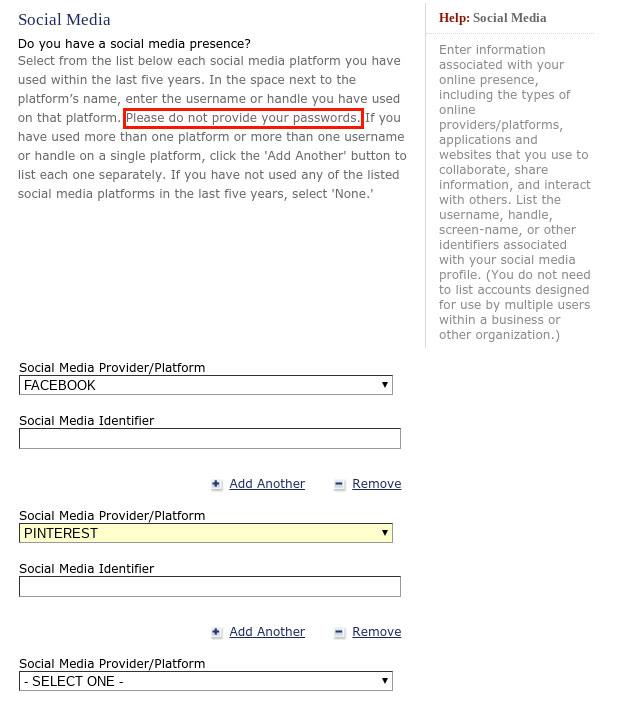
In the ever-shifting landscape of immigration policy, a controversial proposal threatens to redefine the boundaries of personal privacy and digital expression. The Trump administration’s latest directive seeks to compel green card applicants already navigating the complex legal pathways to permanent residency to unveil their digital footprints—a move that could fundamentally alter how immigrants perceive and engage with social media platforms. As pixels and personal narratives become potential gatekeepers of chance, this policy raises profound questions about free speech, surveillance, and the delicate balance between national security and individual rights. In a controversial move that has sparked intense debate, the proposed policy targeting green card applicants threatens to reshape digital communication landscapes for immigrants seeking permanent residency. The initiative would require individuals already legally residing in the United States to disclose their social media profiles, raising meaningful concerns about privacy and potential discrimination.
Legal experts argue that this requirement could create ample barriers for individuals navigating the complex immigration system. By mandating comprehensive digital openness,applicants might feel pressured to self-censor their online interactions,fundamentally altering how they express themselves in digital spaces.
Critics point out that such a policy could disproportionately impact marginalized communities, possibly weaponizing social media content as a mechanism for exclusion. The broad nature of the proposed requirement means that innocuous posts, political opinions, or cultural expressions could be scrutinized through an unpredictable interpretative lens.
Immigration attorneys have highlighted potential constitutional challenges, suggesting that the policy might infringe upon First Amendment protections. The chilling effect on free speech could discourage open dialogue and create an habitat of digital surveillance and self-restriction.
Social media platforms themselves might become inadvertent gatekeepers, with users potentially modifying their online personas to appear more “acceptable” to immigration authorities. This creates a problematic dynamic where digital presentation becomes a performative exercise in conformity rather than authentic self-expression.
The proposed regulation also raises significant technological and administrative challenges. Reviewing potentially thousands of social media profiles would require substantial bureaucratic resources, creating potential bottlenecks in an already complex immigration process.
Technological privacy advocates warn about the broader implications of such policies. The precedent set could normalize invasive digital screening processes across various governmental and institutional contexts, potentially eroding individual privacy rights.
Immigrant communities have expressed particular concern about the potential for bias and subjective interpretation. Social media content often involves nuanced cultural contexts that might be misunderstood by reviewers unfamiliar with specific linguistic or cultural backgrounds.
International observers have noted that such policies could damage the United States’ global reputation as a welcoming destination for talented individuals seeking opportunity. The potential deterrent effect might discourage skilled professionals and researchers from pursuing immigration pathways.
As the debate continues, the proposed policy represents a complex intersection of technological surveillance, immigration policy, and essential rights to privacy and expression. The ultimate impact remains to be seen, but the conversation highlights critical tensions in contemporary digital society.