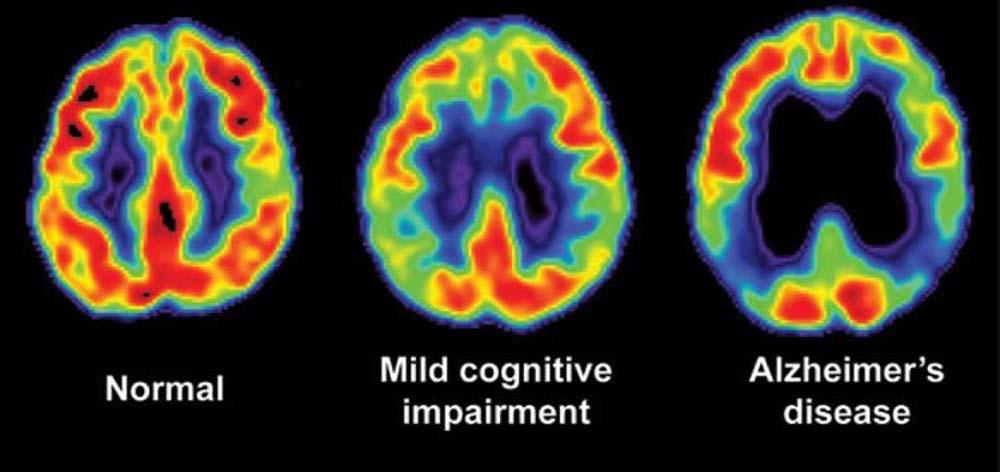
In the labyrinth of human health,where mysteries often lurk beneath the surface,researchers have illuminated a new pathway to understanding dementia—a condition that silently weaves its way through countless lives. Recent scientific revelations have unveiled a warning sign that may be far more prevalent than previously imagined, challenging our perception of cognitive decline and offering a glimmer of hope in early detection. As the medical community peels back another layer of this complex neurological puzzle,patients and healthcare professionals alike lean in,eager to grasp the implications of this groundbreaking discovery. Recent groundbreaking research has revealed an unexpected early indicator of potential cognitive decline that medical professionals are now closely examining. This newly discovered warning sign relates to subtle changes in communication patterns that many people might dismiss as insignificant.
Studies conducted by neurological researchers have found that decreased verbal fluency and specific language alterations could be crucial precursors to developing dementia. Participants who demonstrated difficulty finding words, experiencing more frequent pauses during conversations, or struggling to complete sentences were significantly more likely to experience cognitive deterioration in subsequent years.
Experts emphasize that these communication shifts often occur gradually and can be easily overlooked by family members and even individuals experiencing them.The nuanced changes might initially seem like typical age-related memory lapses,but they represent something more profound and potentially concerning.
Neurologists have identified that language processing involves complex brain networks, and disruptions in these networks can signal underlying neurological changes. When communication becomes increasingly challenging, it might indicate neurological restructuring associated with early-stage cognitive decline.
Researchers tracked multiple patient groups and discovered that approximately 20-25% of individuals showing these communication patterns developed dementia within five to seven years. This statistic underscores the significance of recognizing and monitoring these subtle linguistic transformations.
Medical professionals recommend comprehensive cognitive assessments for individuals experiencing persistent communication difficulties. These evaluations can definitely help distinguish between normal aging processes and potential neurological concerns.
Technological advancements now enable more precise tracking of linguistic patterns. Refined speech analysis algorithms can detect microscopic changes in vocabulary, sentence structure, and verbal fluency that human listeners might miss.
Interestingly, the research suggests these communication shifts are not exclusive to older populations.Younger individuals with genetic predispositions or specific risk factors might also exhibit these early warning signs.Prevention strategies remain crucial. Maintaining cognitive health through regular mental stimulation, social engagement, healthy nutrition, and consistent physical activity can potentially mitigate dementia risks.Healthcare providers encourage individuals and families to pay close attention to communication patterns, documenting any noticeable changes and discussing them with medical professionals. Early detection and intervention remain the most promising approaches in managing potential cognitive decline.
This groundbreaking research offers hope by providing a more nuanced understanding of dementia’s early indicators, potentially revolutionizing diagnostic and preventative approaches in neurological healthcare.