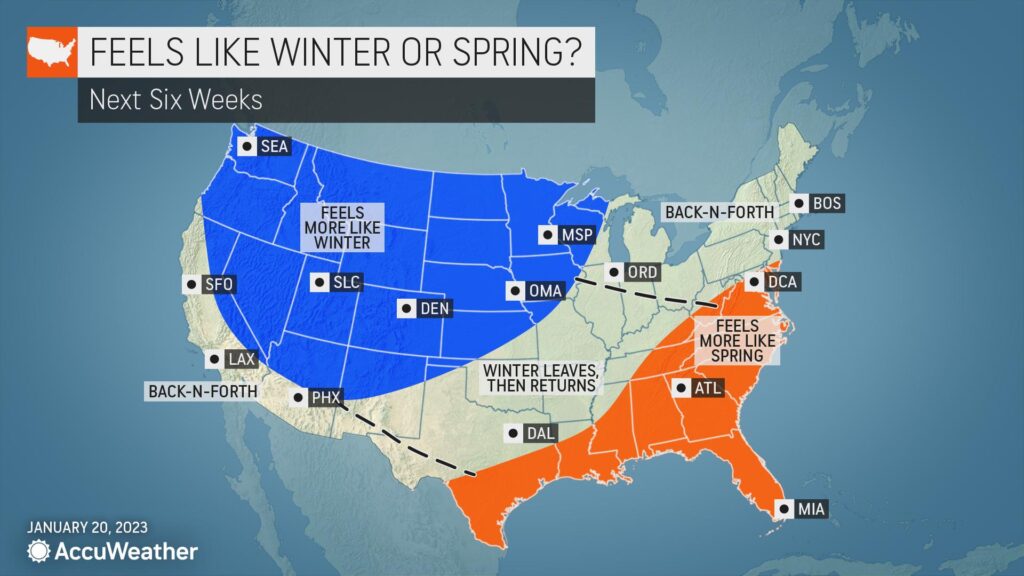
As winter’s icy grip slowly releases its hold, a wave of unusually warm temperatures threatens to paint the American landscape in unexpected hues. Meteorological data suggests a departure from seasonal norms, signaling a potential climate shift that could redefine how we perceive the transition from winter’s chill to spring’s gentle awakening. The mercury is poised to climb, challenging long-established temperature patterns and offering a glimpse into the evolving atmospheric dynamics of the United States. As winter gradually releases its grip, meteorological indicators point to an unusual seasonal transition marked by higher-than-normal temperatures across substantial portions of the United States. Climate experts are forecasting a warmer-than-typical period that could significantly impact regional weather patterns and ecological systems.
The National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration (NOAA) has released preliminary projections suggesting widespread temperature anomalies, particularly concentrated in northern and midwestern regions. These predictions indicate potential temperature increases ranging from 2 to 5 degrees Fahrenheit above historical averages.
Agricultural sectors are closely monitoring these temperature trends, recognizing that early warmth could accelerate planting seasons and potentially disrupt traditional crop cultivation schedules. Farmers might need to adapt their strategies to accommodate these shifting climatic conditions, potentially adjusting seed selection and planting timelines.
Ecological systems will likely experience accelerated transformations, with plant species potentially budding earlier and wildlife migration patterns experiencing subtle shifts. Researchers anticipate these temperature variations could trigger cascading effects throughout regional ecosystems, influencing biodiversity and natural reproductive cycles.
Urban centers may experience distinct microclimatic consequences, with metropolitan areas potentially experiencing more pronounced temperature increases due to heat island effects. Infrastructure planning and energy consumption could be directly impacted by these projected thermal variations.
Climate scientists emphasize that while individual seasonal fluctuations don’t definitively represent long-term climate trends, consistent patterns of elevated temperatures warrant careful observation. The emerging data suggests potential connections to broader global climate change phenomena.
Recreational and tourism industries might see unexpected modifications in seasonal activities. Winter sports regions could experience shortened snow seasons, while outdoor enthusiasts might witness extended periods suitable for hiking, cycling, and other warm-weather pursuits.
Public health professionals are simultaneously tracking potential implications, noting potential increases in heat-related health risks and modifications to seasonal allergy patterns. Early warming could extend pollen seasons and increase respiratory challenges for vulnerable populations.
Meteorological models continue refining their predictions, utilizing advanced computational techniques and expansive data collection networks. These sophisticated forecasting methods enable more precise understanding of emerging temperature trends and their potential societal impacts.
As communities prepare for this anticipated thermal transition, adaptability and proactive planning emerge as critical strategies. Understanding and responding to these nuanced climatic shifts will be essential for maintaining ecological balance and supporting human infrastructure across diverse regional landscapes.